
What are the signs and symptoms of delusional disorder? The most common type of delusional disorder is the persecutory type - when someone believes others are out to harm them despite evidence to the contrary.

What is the most common type of delusional disorder? Approximately 0.05% to 0.1% of the adult population has delusional disorder. These populations include:Īlthough delusions might be a symptom of more common disorders, such as schizophrenia, delusional disorder itself is rather rare. People who tend to be socially isolated are more likely to develop delusional disorder. The persecutory and jealous types of delusional disorder are more common in people assigned male at birth (AMAB), and the erotomanic type is more common in people assigned female at birth (AFAB). Who does delusional disorder affect?ĭelusional disorder most often occurs in middle to late life, with the average age of onset being 40 years. In addition, in contrast to schizophrenia, delusional disorder is relatively rare, and daily functioning isn’t as impaired as it is in schizophrenia.
Negative symptoms (a decrease in emotion in a person’s facial expressions and motivation).ĭelusional disorder is different from schizophrenia because there aren’t any other psychotic symptoms other than delusions. Schizophrenia is a spectrum (or range) of conditions that involve psychotic symptoms, which include: What is the difference between delusional disorder and schizophrenia? Mixed: People with this type of delusional disorder have two or more of the types of delusions listed above. Somatic: People with this type of delusional disorder believe that they have a physical issue or medical problem, such as a parasite or a bad odor. People with this type of delusional disorder may make repeated complaints to legal authorities. Persecutory: People with this type of delusional disorder believe someone or something is mistreating, spying on or attempting to harm them (or someone close to them). Jealous: People with this type of delusional disorder believe that their spouse or sexual partner is unfaithful without any concrete evidence. They may believe they have a great talent or have made an important discovery. Grandiose: People with this type of delusional disorder have an overinflated sense of self-worth, power, knowledge or identity. They may attempt to contact the person of the delusion and engage in stalking behavior. Erotomanic: People with this type of delusional disorder believe that another person, often someone important or famous, is in love with them. The types of delusional disorder include: There are different types of delusional disorder, which are determined based on the main theme of the delusions the person experiences. What are the types of delusional disorder? In some cases, however, people with delusional disorder might become so preoccupied with their delusions that their lives are disrupted. This is unlike people with other psychotic disorders, who might also have delusions as a symptom. Generally, they don’t behave in an odd or unusual manner. People with delusional disorder often continue to socialize and function well, apart from the subject of their delusion. Non-bizarre delusions are different from bizarre delusions, which include beliefs that are impossible in our reality, such as believing someone has removed an organ from your body without any physical evidence of the procedure. In reality, these situations are either untrue or are highly exaggerated. 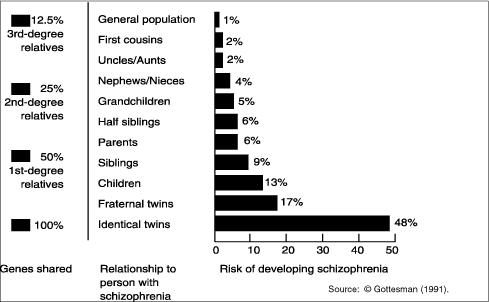
These delusions usually involve the misinterpretation of perceptions or experiences. Non-bizarre delusions involve situations that could possibly occur in real life, such as being followed, deceived or loved from a distance. People with delusional disorder often experience non-bizarre delusions. The belief isn’t a part of the person’s culture or subculture, and almost everyone else knows this belief to be false. Its main symptom is the presence of one or more delusions.Ī delusion is an unshakable belief in something that’s untrue.
Delusional disorder is a type of psychotic disorder.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
